Uterine fibroids can cause your uterus to enlarge and make other changes to your body which can be uncomfortable. If you think your extending abdomen and other symptoms are being caused by growing uterine fibroids, schedule an appointment with Dr. Sergei A. Sobolevsky at Downtown Vein & Vascular Center. He helps you understand what fibroid size is considered big, what complications it can cause, and what treatment options can help to get rid of these tumors safely and effectively. Dr. Sobolevsky understands that too big fibroids may become a serious health issue and comes up with the best solutions to prevent them to ensure you get back control of your life.
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous tumors that grow in the uterus. They develop in women of reproductive age and are extremely common. The fibroid size can vary from less than an inch to larger than a grapefruit. Large fibroids can expand a normal sized uterus to a size large enough to make the woman’s abdomen bulge out. They can also worsen symptoms and cause medical issues for many women if they are not treated timely.
Read on to understand if fibroid size really matters, how big they grow, how they affect your health, and what treatment options work best to remove a large fibroid.
How Big Can a Fibroid Get?
Uterine fibroids can range in size from a small bead to as large as a small watermelon, and they can develop in numbers. Where a single fibroid may be less than an inch, groups and clusters of fibroids can be much larger.
A 6-cm fibroid is considered to be the bottom measurement in the classification of large fibroids. They are round and hard as rocks and composed of smooth muscle and fibrous tissue. Depending on their size and location, they can affect various parts of the body. They also expand the uterus so that it impacts other organs or blocks the fallopian tubes, causing problems in conceiving.
Sizes of uterine fibroids range from small to large:
- Small Fibroids – They can be less than 1 cm to 5 cm (.39 to 1.96 inches), the size of a seed to a cherry.
- Medium Fibroids – They range from 5 cm to 10 cm (1.96 to 3.93 inches), the size of a plum to an orange.
- Large Fibroids – These can be 10 cm (3.9 inches) or more, ranging from the size of a grapefruit to a watermelon. Large fibroids cause stomach to distort to the point where a woman may look pregnant.
Even though size is a major indicator of the potential for damage, there is no guarantee that larger fibroids will cause serious problems or that smaller fibroids are harmless and won’t cause any complications. It is also important to note that fibroids can shrink over time, particularly when women hit menopause.
Read more: Average Uterus Size & How Fibroids Change It
Dangers of Fibroids – Are Large Fibroids More Dangerous to Your Health?
Fibroids themselves are not life-threatening. Smaller fibroids do not present any symptoms or cause problems. However, large fibroids can cause discomfort by taking up the space meant for other organs and causing symptoms that a small fibroid cannot by pressing on the abdomen, bladder, and bowel.
Symptoms of a large fibroid include:
- Abdominal enlargement
- Bloating
- Weight gain
- Urinary issues; either feelings of urgency or inability to empty the bladder
- Constipation
The location of fibroids also has a significant impact on the symptoms than their size or numbers. For instance, if a fibroid develops near the endometrial canal, the inner lining of the uterus, it will lead to bleeding. How you feel, and the symptoms you experience make fibroids more dangerous. Very large fibroids can also make the abdomen bulge out, which makes you feel embarrassed.
Every women’s experience with fibroids is different. Consulting a healthcare professional is necessary to assess how these fibroids affect the quality of life and everyday comfort.
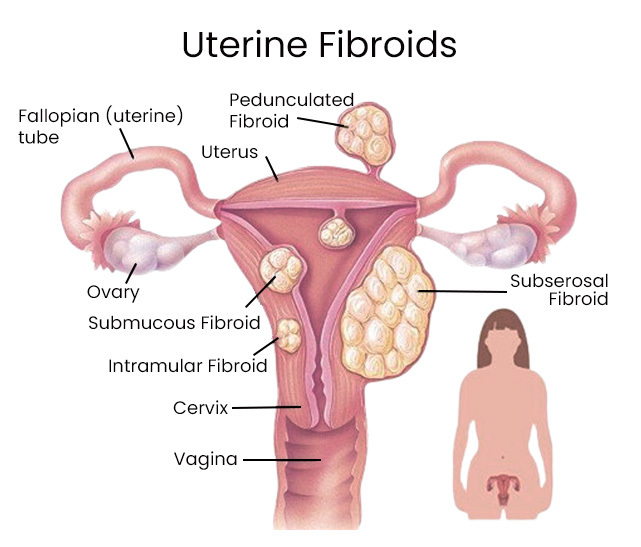
Types of Fibroids
There are four types of uterine fibroids.
They are:
- Intramural fibroids – They are the most common type of fibroids that grow in the wall of the uterus.
- Subserosal fibroids – These fibroids grow on the outside of the uterine wall. As they grow larger, they can cause pressure on nearby organs or pain due to their size.
- Submucosal fibroids – They grow just underneath the uterine lining and can crowd into the uterine cavity, leading to heavy bleeding and other, more serious complications. These are the rarest type of fibroids.
- Pedunculated fibroids – These fibroids grow on small stalks or stems and can develop either outside the uterus or inside the uterine cavity.
Estrogen is believed to be the primary reason for stimulating fibroids in most cases. In fact, during the first trimester of pregnancy, about one-third of fibroids will grow larger, but they will shrink after birth. Fibroids also shrink after menopause, but postmenopausal hormone therapy can result in fibroid growth.
Around 70 to 80% of women develop a fibroid tumor by the time they reach age 50. It is important to note that you may also develop more than one type of fibroid, depending on their causes and underlying causes.
Read more: What Is A Vein Specialist Called?
Fibroid Size – How Big Is Too Big?
Most women with uterine fibroids have an enlarged uterus. Doctors describe the size of fibroids and their effect on a woman’s uterus as would a pregnancy such as a 14-week-sized fibroid uterus. A fibroid-affected uterus can grow up to the size of a four- to five-month pregnancy, which can be really uncomfortable and awkward.
A fibroid is considered giant if it weighs 25 pounds or more, which is similar to carrying around a child. Carrying a fibroid of this size is not only uncomfortable, but also causes embarrassment. The good news is that once the fibroids are removed, the uterus returns to its original size, relieving the symptoms.
Evaluating Uterine Fibroid Size for Removal
Without a proper diagnosis by a specialist, it is tough to determine the fibroid size. Fibroids that make the abdominal or belly area protrude indicate that you have larger tumors. A healthcare provider can make an accurate diagnosis regarding the presence and size of fibroids with the help of an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.
Depending on the size of the fibroid and the symptoms it is causing, your top fibroid doctor near me will determine whether it needs to be removed. Treatment is necessary to prevent the fibroids from growing to a size that results in painful symptoms. Large fibroids or fibroids that continue to grow can lead to several complications.
They include:
- Reproductive problems if submucosal fibroids are found on the inside of the uterus and are large enough to misshape the uterine lining.
- Risk of injury or complications to the bladder or ureter in case of surgery if fibroids are larger than a 12- to 14-week pregnancy or the size of a large grapefruit.
- Degeneration of very large fibroids if they are left untreated, even if they are not causing any symptoms. Sometimes these fibroids also burst when the growing fibroid outgrows its blood supply, causing the cells of the fibroid to die, causing severe pain and tenderness.
- A risk of blood clots in the lungs that can be deadly if the fibroids reach the size of a grapefruit.
- Development of a rare cancerous form of fibroid, called a leiomyosarcoma, if the fibroid continues to grow rapidly. This type of tumor is not believed to develop from a benign fibroid and is difficult to diagnose.
Treatment Options for Uterine Fibroids
There are several options for treating uterine fibroids.
They include:
- Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) – It is the most prevalent non-invasive treatment for fibroids. Tiny particles about the size of sugar crystals are injected into the blood vessels that lead to the uterus. The particles block the flow of blood to the fibroid, causing it to shrink and die. This procedure can be performed on any fibroid size and relieves symptoms with fewer risks, less pain, and a faster recovery, as compared to surgical procedures.
- MRI-guided ultrasound surgery – This procedure uses ultrasound waves to destroy fibroids. Waves are directed at the fibroids through the skin with the help of magnetic resonance imaging.
- Endometrial ablation – It destroys the lining of the uterus. This procedure is best for small fibroids that are less than 3 centimeters in diameter.
- Hysterectomy – It is the surgical removal of the uterus from the body. As it removes the fibroids along with the uterus, there is no chance of becoming pregnant after this procedure.
- Myomectomy – It is another surgical option to remove all types of fibroids. There are three approaches to performing a myomectomy that can remove fibroids, preserve fertility and offer relief from symptoms. However, around 30% of patients may grow new fibroids and require surgery again after a few years.
Your healthcare provider will recommend the most effective uterine fibroid treatment option keeping in mind the location and size of your fibroids and the dangers they pose to your health. It is essential to fully understand the risks associated with surgery as well as the benefits of minimally invasive alternative treatments to make the best decision.
Visit Downtown Vein & Vascular Center for detailed information on how big uterine fibroids can grow, how you can prevent them, and what treatment options work best for removing them safely, without damaging your uterus. Dr. Sergei A. Sobolevsky has been helping women with fibroids for years and understands your health concerns if you have been diagnosed with fibroids. He makes treating your tumors both easy and convenient by recommending the most effective options, depending on your age, uterus size, and your plans regarding future pregnancies.


