If you are bleeding extensively and it lasts more than 7 days, it means you are having a heavy period. Schedule an appointment at Downtown Vein & Vascular Center to find out what is causing your heavy periods and if it is some underlying medical condition behind your symptoms. Dr. Sergei A. Sobolevsky evaluates your symptoms of menorrhagia and provide the best possible advice. He also recommends home remedies and support tools to manage heavy bleeding to ensure you live as easy a life as possible, even during your period.
A couple of heavy flow days at the beginning of your period is common. But if you have to change sheets in the morning because you bleed through your tampon or pad at night, avoid wearing light-colored clothing during your cycle or always carry extra tampons, you may have chronic heavy periods.
Read on to know what may be causing your heavy period, how to tell the difference between standard or excessive menstruation bleeding, and what treatment options can help you deal with it in the best possible manner.
Read more: Checking Yourself for DVT At Home
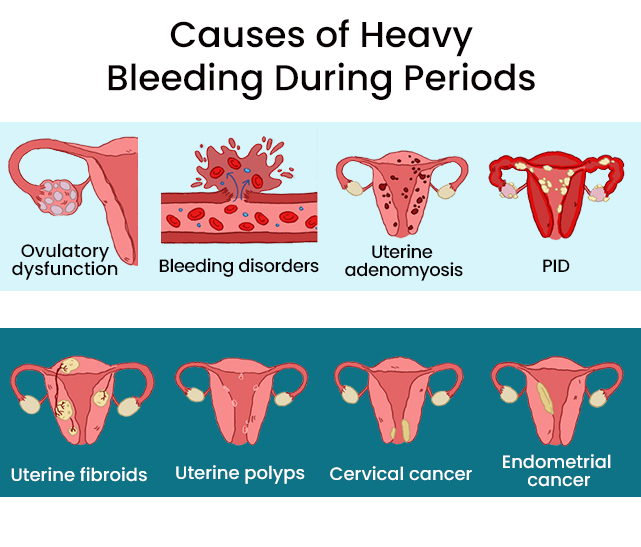
Causes of Heavy Bleeding During Periods?
Menstrual bleeding that is so heavy that it interferes with your daily life is not normal. There are different causes of heavy bleeding during periods. The good news is that none of these causes is serious, and they can be treated at home or with medications. As each women’s body is unique, consulting a doctor is the only way to learn the reason behind heavy periods.
Some of the most common causes of heavy periods include:
- Life changes – Our bodies are sensitive to change, and any deviation from routine life events can lead to abnormal periods. Even stress can affect your cycle and flow and result in heavy bleeding. Most women report heavy period flow after pregnancy or childbirth or the time their body transitions to menopause.
- Changes to medication or birth control – Changes to medications can result in heavy periods, particularly if you are taking a blood thinning medication. Even switching to a new form of birth control can affect the length of your menstrual cycle and how much you bleed. In some women, using a copper or hormonal intrauterine device, IUD can cause heavy periods for 3 to 6 months after insertion.
- Hormonal imbalance – Too little or too much estrogen and progesterone hormones can lead to menorrhagia. Some women experience high levels of estrogen and low levels of progesterone. It can thicken the uterine lining, and when this thick uterine lining sheds during menstruation, it causes heavier blood flow and larger blood clots.
- Uterine fibroids – Fibroids are small, non-cancerous growths inside the uterus. Their size ranges from a grain of sand to a large mass that can affect the size of your uterus and bleeding.
- Endometriosis – It is a painful condition that causes abnormal growth of the uterine lining and forms uterine polyps. It can cause short period cycles and heavy, painful periods as the body sheds the thickened uterine lining.
It is best to talk to your doctor if you notice unusual changes to your period or blood flow, particularly after starting a new medication, changing birth control, or after some stressful event.
What Is Menorrhagia?
Heavy menstrual flow is medically known as menorrhagia. A female with menorrhagia may need to change her pad or tampon every hour or many hours in a row. Large blood clots may regularly appear in the menstrual flow.
Heavy periods are normal for some women, but for others, they can be pretty disturbing. Not only do they affect life and take a toll on the body, but they also make you feel very tired and cause more pain and cramping. In some women, heavy periods lead to excessive blood loss and anemia. You must talk to your doctor if you are losing too much blood in periods or having big blood clots to identify any underlying cause.
It comes as a surprise to many, but about one in five women experience menorrhagia. Since everyone is different, knowing what is normal for your cycle or if you are having a heavy period may be difficult. Half of the women who experience menorrhagia do not even realize they have it.
According to healthcare experts, any of the following can be considered a symptom of heavy menstrual bleeding:
- If you are bleeding for more than seven days
- If you are bleeding through one or more tampons or pads every hour
- If you are changing your pad or tampon during the night
- If you have to double up on protection to keep from leaking
- You notice blood clots the size of a quarter or larger
- Abdominal pain
If left untreated, heavy-period bleeding can also lead to anemia, a condition in which you don’t have enough red cells to circulate the amount of oxygen needed by the body.
It can cause other physical symptoms, including:
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
Talk to your doctor if your heavy periods are chronic to prevent anemia and other health complications that can turn life-threatening without treatment.
How Is Menorrhagia Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis of menorrhagia depends on confirming that your bleeding is unusually heavy and identifying its underlying cause. Your doctor will do a physical exam, particularly a pelvic exam, and question you about your medical history and menstrual cycle to determine heavy menstrual bleeding. He may also run additional tests and non-invasive procedures to diagnose abnormal bleeding and underlying issue.
They include:
- Blood test – To check hormone levels and look for signs of anemia or clotting.
- Pap test – Cells from your cervix are examined for signs of infection, inflammation, or other unusual changes.
- Endometrial biopsy – Samples are collected from your uterine lining and tested for the presence of any unusual or cancerous cells.
- Ultrasound – It checks for dysfunction in the pelvic organs, as well as blood flow issues.
- Sonohysterogram – It is another kind of ultrasound that is performed while the uterus is filled with liquid to get a better look at the uterine lining.
- Hysteroscopy – It is a non-invasive procedure in which a tiny, flexible camera examines the uterus for fibroids, polyps, and other possible causes of bleeding issues.
Learn available fibroid treatments in Brooklyn our specialists offer:
- Highly effective management of uterine fibroid pain
- Management of frequent urination caused by fibroids
- Uterine fibroid embolization or UFE
- Uterine fibroid surgery
Our top vein doctors also provide vein treatments in Downtown Brooklyn, NY, such as:
How to Stop Heavy Periods?
Knowing the underlying reason for your heavy periods is key to getting the treatment that will work best for you. Talking to a doctor is necessary as treatment depends on what is causing your bleeding and how severe it is, as well as your health, age, and medical history.
Menorrhagia Treatment
Treatment for menorrhagia is based on several factors, including:
- Your overall health and medical history
- The cause and severity of the condition
- Your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies
- A probability that your periods will become less heavy soon
- Your plans regarding pregnancy and childbirth
- Effects of menorrhea on your lifestyle
- Your personal preference
For most women, menorrhagia treatment is a matter of medications and some lifestyle changes.
They include:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – NSAIDs help to reduce the pain caused by menorrhagia and make the periods lighter. It is because they decrease the number of prostaglandins, hormones that cause pain and bleeding in your uterine lining. However, it is crucial to consult your doctor before taking NSAIDs as some of them have blood thinning effects and may worsen the bleeding.
- Birth control – Hormonal birth control can help to regular your periods and lighten the flow.
- Pills, patches, hormonal IUDs, and other forms of hormonal contraceptives can thin the uterine lining, which reduces the amount of blood and tissue you lose during the menstrual cycle. Birth control is effective in regulating the length of your cycle, easing painful cramps, or even stopping the period altogether. It can also help to manage menopause symptoms if you are entering perimenopause or menopause.
- Hormonal therapy – Hormone therapy can reduce bleeding if heavy periods are resulting from hormone imbalance. Like hormonal birth control, regular hormone therapy can thin the uterine lining and balance the hormones. It can also treat conditions like endometriosis that cause pain and menstrual bleeding.
- Medications – Prescription medications can treat menorrhagia symptoms. Your doctor may prescribe stronger NSAIDs, tranexamic acid, and desmopressin. Tranexamic acid can be taken at the start of a menstrual period to reduce bleeding, while desmopressin reduces bleeding by clotting the blood.
- Dietary changes – Eating a diet rich in iron can prevent anemia and other complications that result from menorrhagia. Include iron-rich foods like meat, seafood, beans, nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables in your diet. Also, foods rich in vitamin C, like oranges, bell peppers, and broccoli, help the body absorb extra iron. It is essential to avoid processed sugar, trans-fats, and starchy carbs as they can worsen the menorrhagia symptoms.
Read more: Why Leg Cramps Happen & When To Worry
When Should You See a Doctor for Heavy Periods?
Heavy periods are not something you should be living with. If they are disturbing your daily life, school work, and social activities, or you are forced to plan your day around bathroom breaks, it is time to seek medical help.
The doctor will ask questions about your medical history and menstrual cycle and evaluate your symptoms to diagnose your condition. Based on the causes of your heavy period, the doctor will recommend effective treatments to stop the unnecessary loss of blood. Your doctor is likely to recommend surgical procedures if there are growth or polyps in the uterus to treat period issues.
Heavy periods are common, but this does not mean you have to live with the discomfort they cause or reschedule your routine activities. Unusual blood flow can affect your emotional and physical well-being and even turn life-threatening if you lose too much blood. If your heavy period is worrying you, consult Dr. Sergei A. Sobolevsky to learn about treatments and various techniques for managing menorrhagia. Dr. Sobolevsky is an experienced endovascular specialist and focuses on issues related to blood vessels and circulation. He also looks for underlying issues, along with making a confirmed diagnosis to reduce the intensity and duration of the flow to provide desired relief.

Sergei Sobolevsky, MD, is a leading specialist in endovascular medicine with experience in vascular and interventional radiology. Dr. Sobolevsky has decades of experience in the field, with over 25,000 procedures performed, accumulating extensive experience in image-guided minimally invasive medicine, diagnosing and treating a range of conditions.
Dr. Sobolevsky earned his Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree in 1997 from the University of Colorado School of Medicine. He received his specialty clinical training in vascular and interventional radiology at Harvard University. Later, he earned his MBA from the MIT Sloan School of Management. Recognized as a Castle Connolly Top Doctor and named to the Top Doctors New York Metro Area in 2020, 2021, and 2022, Dr. Sobolevsky is licensed in multiple states, has delivered presentations at numerous institutions in the US and abroad, and now acts as a clinical advisor for the biomedical industry. He also held multiple positions in the field during his career, including Chief of Vascular and Interventional Radiology at the Columbia University Medical Center in New York, NY, Senior Vice President in Clinical and Regulatory Affairs at Artann Laboratories in North Brunswick, NJ, and Medical Director at the American Endovascular and Amputation Prevention Center in Brooklyn.
More About Dr. Sobolevsky
